JVEssentialClasses
This page gives an overview over some essential JavaView packages and classes that are fundamental in most applications.jv.vecmath
The vecmath package provides classes and methods for linear algebra and simple vector calculations. Important classes arejv.vecmath.PdVector // Class for an array of double values. jv.vecmath.PiVector // Class for an array of integer values . jv.vecmath.PdMatrix // Class for a small (m,n)-matrix of double values jv.number.PdColor // Class for a color with red, green and blue components
jv.vecmath.PdVector
A point or a vector in 3D respectively nD space can be represented with an instance of PdVector. A vector also provides several methods for linear algebra calculations.
class PdVector {
double [] m_data; // array of double values
// constructs a vector with given size
PdVector(int dim) {
m_data = new double[dim];
}
// constructs a vector with two entries
PdVector(double x, double y) {
m_data = new double[] {x, y};
}
// retrieve a single array component at given index
double getEntry(int ind) {
return m_data[ind];
}
}
Sample usage:
PdVector v = new PdVector(1., 0.); PdVector w = new PdVector(0., 1.); v.add(w); double norm = v.length();
PdVector v = new PdVector(1., 0.); PdVector w = new PdVector(0., 1.); v.add(w); double norm = v.length();This type also serves as a list for doubles. It can have several flags set. For instance if
p is a PdVector which is a point of geom, then p.hasTag(IS_SELECTED) is true iff p is currently selected/marked on the display. In addition it comes with many methods for common vector calculations such as dot and cross product, length, distance, orthogonal projections and so on. Also check the static methods!
jv.vecmath.PiVector
Similar toPdVector, but for integers. May be used as a list/stack for integer values. Use instead of List. New entries can be added to list by calling aPiVector.addEntry(n). This will append the number $n$ to the list. Don't confuse with aPiVector.add(x) which adds the value x to each entry of the vector. An interesting method is removeSuccessiveDuplicates() which does what its name says.
jv.geom
The geom package provides classes and methods for widely used geometry containers such as sets of points, polygons and faces. Important classes arejv.geom.PgPointSet // Class for a set of points in 2D, 3D, or nD space. jv.geom.PgPolygon // Class for a single polygon. jv.geom.PgPolygonSet // Class for a set of polygons sharing points jv.geom.PgElementSet // Class for a surface of planar polygonal faces jv.geom.PgVectorField // Class for a vector field associated to a base geometry jv.geom.PgTexture // Class for a texture image
jv.geom.PgPointSet
A set of points in either 2d, 3d, or any n-dimensional ambient space. All points in a point set must have the same dimension.
class PgPointSet {
int m_dim; // uniform dimension of each point
PdVector [] m_vertex; // array of all points
PdVector [] m_vertexNormal; // optional, a normal vector at each point
PdColor [] m_vertexColor; // optional, a color of each point
PdVector [] m_vertexTexture; // optional, a texture position of each point
// constructor specifies dimension of ambient space
PgPointSet(int dim) {
m_dim = dim;
}
// allocate a set of vertices (and, if exist, vertex normals and colors)
void setNumVertices(int num) {
m_vertex = new PdVector[num];
for (int i=0; i<num; i++)
m_vertex[i] = new PdVector(m_dim);
}
}
Sample usage:
PgPointSet ps = new PgPointSet(2); ps.setNumVertices(3); ps.setVertex(0, 1., 0.); ps.setVertex(1, 2., 1.); ps.setVertex(2, 0., 3.);
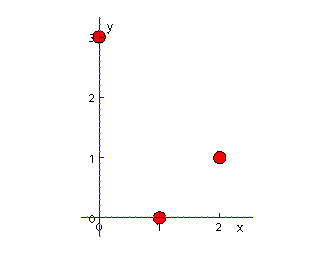
jv.geom.PgElementSet
Polyhedral surface in n-dimensional space is based on a point set.
class PgElementSet extends PgPointSet {
PiVector [] m_element; // array of faces
PdVector [] m_elementNormal; // optional, a normal of each face
PdColor [] m_elementColor; // optional, a color of each face
PdVector [] m_elementTexture; // optional, a texture position of each point
// constructor specifies dimension of ambient space
PgElementSet(int dim) {
super(dim);
}
// allocate a set of facees (and, if exist, element normals and colors)
void setNumElements(int num) {
m_element = new PiVector[num];
// note: size of individual of elements not known yet
}
}
Sample usage:
PgElementSet es = new PgElementSet(2); // Use points of previous point set es.copy(ps); es.setNumVertices(4); es.setVertex(3, 2., 3.); // Define two triangles es.setNumElements(2); es.setElement(0, 0, 1, 2); // vertex indices of first face es.setElement(1, 2, 1, 3); // vertex indices of second face double area = es.getArea();
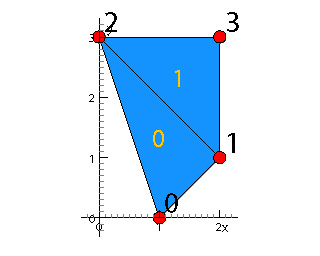 Additional useful member methods:
Additional useful member methods: -
geom.getVertices(): Returns a list of the vertex indices -
geom.showElementColors(true/false): enables the display of individual element colors in contrast to the global element color which is shown by default. The same story withgeom.showVertexColors(true/false). -
geom.showVertices(true/false): Displays the vertices of the geometry. -
geom.setVertexColor/Size/...: Sets individual vertex properties such as color or size. Make sure you have enabled display of individual vertex colors by callinggeom.showVertexColors(true)before. -
geom.getElement(i): Returns aPiVectorof integers of the vertex indices forming the element with index i.
jv.viewer
Provides functionality for the display and related managing tasks. Important classes:jv.viewer.PvDisplay // Class for a single display for viewing. jv.viewer.PvControl // Class is a panel to hold several inspectors. jv.viewer.PvViewer // Manages several displays and a control panel. jv.viewer.PgAxes // Utility class for the coordinate axis and labels. jv.viewer.PvCamera // Utility class for a single camera. jv.viewer.PvLight // Utility class for a single light.
jv.viewer.PvDisplay
A display is a drawing canvas which shows a collection of geometries:
class PvDisplay extends Canvas {
// add a geometry to the scene
void addGeometry(PgGeometryIf geom) { ... }
// adjust the scene
void showAxes(boolean flag) { ... }
void setCamera(int type) { ... }
Sample usage:
PvDisplay disp = new PvDisplay(); disp.addGeometry(es); disp.setBackground(Color.red); // insert display to applet (java.awt.Applet or java.awt.Frame) applet.add(disp);You can get the currently selected (i.e. active) geometry by
PgElementSet activeGeom = (PgElementSet) m_display.getSelectedGeometry();
jv.number
Utility classes for inspectable numbers and colors. A double or integer may have a slider, and a color may have an color inspector.
Important classes:jv.number.PuDouble // Class for a single double with slider. jv.number.PuInteger // Class for a single integer with slider. jv.number.PdColor // Class for a color with red, green and blue componentsThese classes provide wrapper for the corresponding native types
int, double and so on. They can register action listeners to react on events and ship with a default inspector panel which can be obtained and added to the project info panel using the getInfoPanel() member method. Make sure that this is done in the info panel class' setParent() method, since you need to access the project class instance most likely.
jv.number.PdColor
This class is the JavaView implementation representing a color. Apart from the methods already provided byjava.awt.Color it has many additional functions e.g. for conversion, creation and blending between different color formats, both as member methods and static functions.
jv.anim
Animation dialog and containers classes for keyframe animation. Important classes:jv.anim.PsAnimation // Class with a play control triggers animated geometries. jv.anim.PsKeyframe // Container class for a keyframe animation.
jv.loader
Import and export classes for reading and writing of geometry files. More loader are provided in extension packagesjvx.loader and elsewhere. Important classes:
jv.loader.PgLoader // Optional loader manager determines the correct loader. jv.loader.PgJvxLoader // Class for reading/writing a JavaView JVX file. jv.loader.PgObjLoader // Class for reading/writing a Wavefront OBJ file. jv.loader.PgMathLoader // Class for reading/writing a Mathematica file.
Functional Geometric Shapes
jvx.surface
jvx.surface.PgDomain // Class is rectangle in the (x,y) plane. jvx.surface.PgGraph // Graph surface of one scalar function on a planar rectangle. jvx.surface.PgParmSurface // Surface of three scalar functions (u(x,y),v(x,y),w(x,y)). jvx.surface.PgSurfaceOfRotation // Parametrized surface of rotation
jvx.geom
jvx.geom.PgBezierCurve // Polygon determined by control points jvx.geom.PgTube // Tube surface around a associated polygon jvx.geom.PgPolygonOnElementSet // Polygon which lies on an associated element set
dev.primitive
Contains many more functional geometry classes which support the JVF format. Will be discuss later.Algorithms and Workshops
The advanced algorithms are kept separately from the geometry classes in so-called workshop classes. Workshops will take a, usually a single, geometry and perform some operations on the geometry. When done the workshop is closed.
Workshops derive from a base class which optionally stores a backup geometry and which simplifies the interaction with a user dialog.
jvx.project.PjWorkshop // Base class for workshops, handles CANCEL and RESET
jvx.geom
jvx.geom.PwClip // Clips a surface at a user defined level function jvx.geom.PwGeodesic // Computes geodesic curves on a surface jvx.geom.PwLIC // Visualizes a vector field on a surface using textures jvx.geom.PwNoise // Adds random noise to vertices of a surface jvx.geom.PwExplode // Explodes a surface into parts jvx.geom.PwSeeds // Investigates a vector field using particles jvx.geom.PwUnfold // Unfolds a surface to a planar region
Projects
A collection of advanced applications. Each application is given by
jv.project.PjProject // Base class for projects with support for pick events
The vgp Package
Contains more than 50 elaborated research applications as well as tutorials including
vgp.tutor.PjFractalImage // Computes Mandelbrot and Julia fractals vgp.tutor.PjTorusKnot // Curves winding around a torus vgp.minimal.weier.PjWeierstrass // Classic minimal surfaces given by Weierstrass equations vgp.game.life.PjLife // Games of life on a surface in 3D. vgp.discrete.harmonic.PjHarmonic // Discrete harmonic maps
Comments
Contains all essential classes from Chapter 2-5. of manual.pdf as of March 2015.
-- KonstantinPoelke - 30 Apr 2015Sitemap
 Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors. Ideas, requests, problems regarding Foswiki? Send feedback